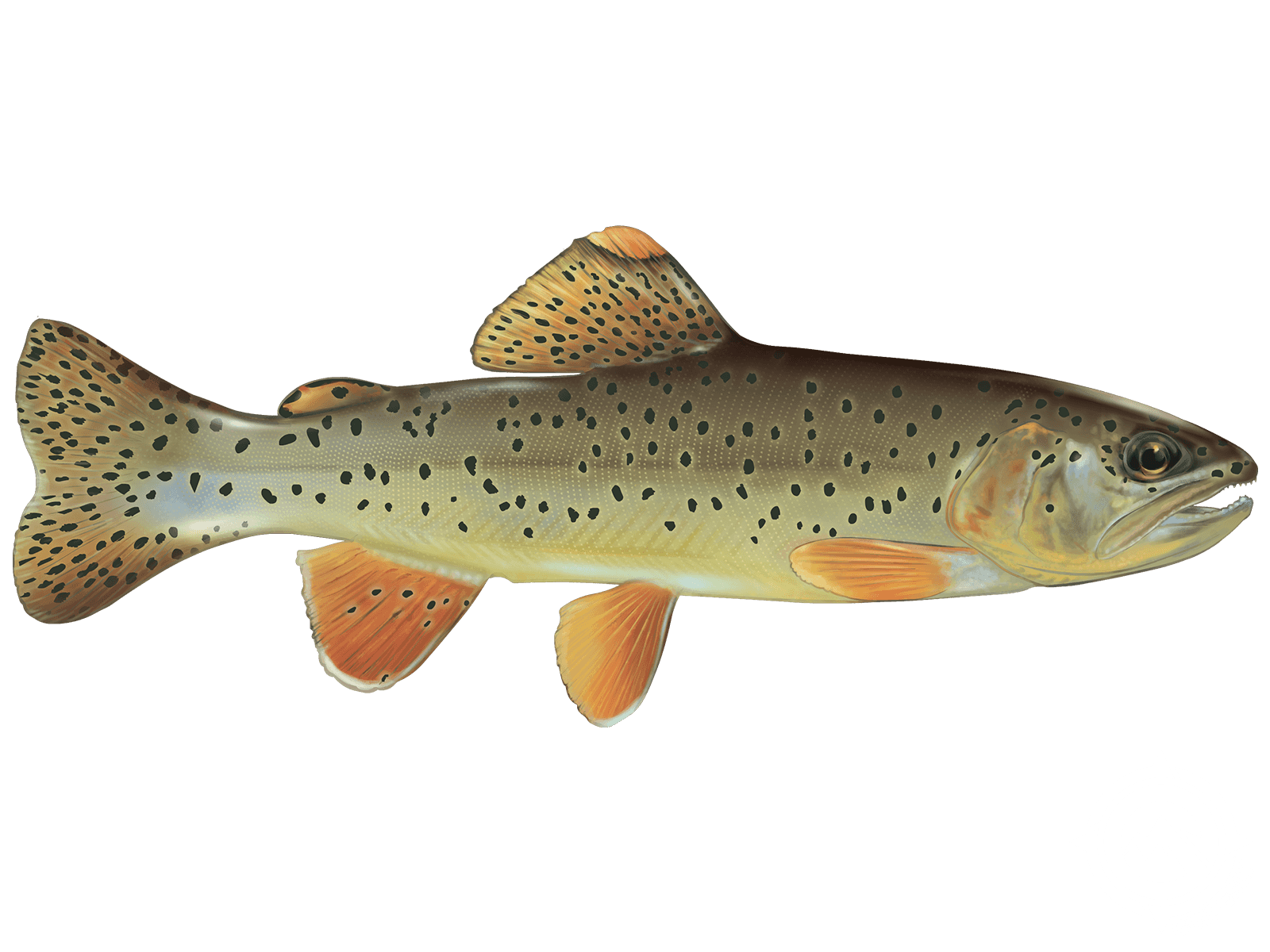
Apache Trout

Species Details
Oncorhynchus Apache
Salmonidae
Salmoniformes
River, Mountain Stream
3 - 6 lbs.
12" - 24"
Apache Trout (Oncorhynchus Apache)
Description
Apache Trout are yellowish-gold in color and has medium-sized dark spots that are equally spaced and can extend below the lateral line onto the tail and dorsal fins. The upper part of the head and back are dark olive and has what appears to be a black stripe on each eye. It is due to two small black dots on both sides of the pupil. There is a slash mark under the lower jaw ranging from yellow to gold in color.
Size
The average size of an Apache Trout range from 12 to 23 inches and weighs between 3-6 pounds. The world record catch was from Hurricane Lake in 1993. It measured 24 inches in length and about 5 pounds in weight.
Interesting Facts
The native Apache Trout's nickname is Arizona Trout as it's only found in Arizona.
Apache trout is one of the two types of trout species native to Arizona. The other native trout is the Gila Trout.
The Apache is found in the streams of the Apache Reservation land and White Mountain Lakes, which are situated in the eastern part of Arizona. It is the state fish of Arizona.
The Apache Trout are able to reproduce with the Cutthroat and Rainbow trout, which were introduced in 1898 to Arizona. This crossbreeding ability has greatly reduced the Apache Trout population, which is the main reason the fish was considered to be at high risk of extinction. However, Apache Trout conservation efforts are helping the trout return to its place in the legacy of Arizona wildlife. Because the species has recovered sufficiently, anglers can now fish for them in designated areas of state waters or on the Fort Apache Indian Reservation.
Spawning
Apache Trout spawn during the spring as most trout. The female fish pairs up with a mate over the gravel layer of the stream and, with their tails, dig a nest in the substrate. There they lay their eggs, and then the male expresses milt over the eggs. The males will defend and pursue other rival males away from the nest and the female. The larvae hatch from the eggs 30 days after deposition. They burrow into the gravel, and approximately 30 days after that, the fry leaves the gravel.
Diet
Apache Trout feed on mostly aquatic insects, small fish, and zooplankton.
Fishing Method and Lures - How to Catch Apache Trout
The angler will find the best results when using types of fishing nymphs, worms or salmon eggs, and wet or dry flies. The fish will also respond well to spinners and spoons. If you are familiar with the more common Rainbow Trout, you will find success with the same techniques. If pole fishing, use a light, strong, and powerful Carbon Pole Rod. If Fly fishing, the angler here can use various methods; wet or dry flies, small lures, or natural baits. However, you may find the artificial flies will produce the best results. Wet flies with small hooks in sizes 14 through 18, usually work better, especially throughout the day. The main essential thing to remember when fishing Apache trout is to use light line, small hooks, and small sinkers.
Habitat
Apache Trout live in water with a high content of dissolved oxygen. They are found in the cold river waters, tributaries, and lakes. They tend to congregate in rock or boulder pockets, where there are low hanging trees and drop-offs.
Distribution
Apache Trout is native to the White Mountain region of Arizona. The North Fork and East Fork of White River join at Fort Apache to form the White River. The White River then flows into the Black River, creating the Salt River. They can be found in all those areas. With the Apache Trout population in jeopardy, the stocking and restoration programs in Arizona have introduced the Apache Trout species to other areas of Arizona including the Little Colorado River and its tributaries, and near the Greer and Lee Valley Lakes.