Bermuda Sea Chub
Species Details
Kyphosus Sectatrix
Kyphosidae
Perciformes
Onshore, Nearshore, Reef
2 - 5 lbs.
12" - 24"
What tips and techniques should I use to successfully catch Bermuda Sea Chub?
When fishing for Bermuda Sea Chub, it's essential to focus on rocky areas, reefs, and nearshore structures. Use lightweight spinning gear with small hooks and bait such as shrimp, squid, or cut bait. Patience is key, as Bermuda Sea Chub can be skittish.
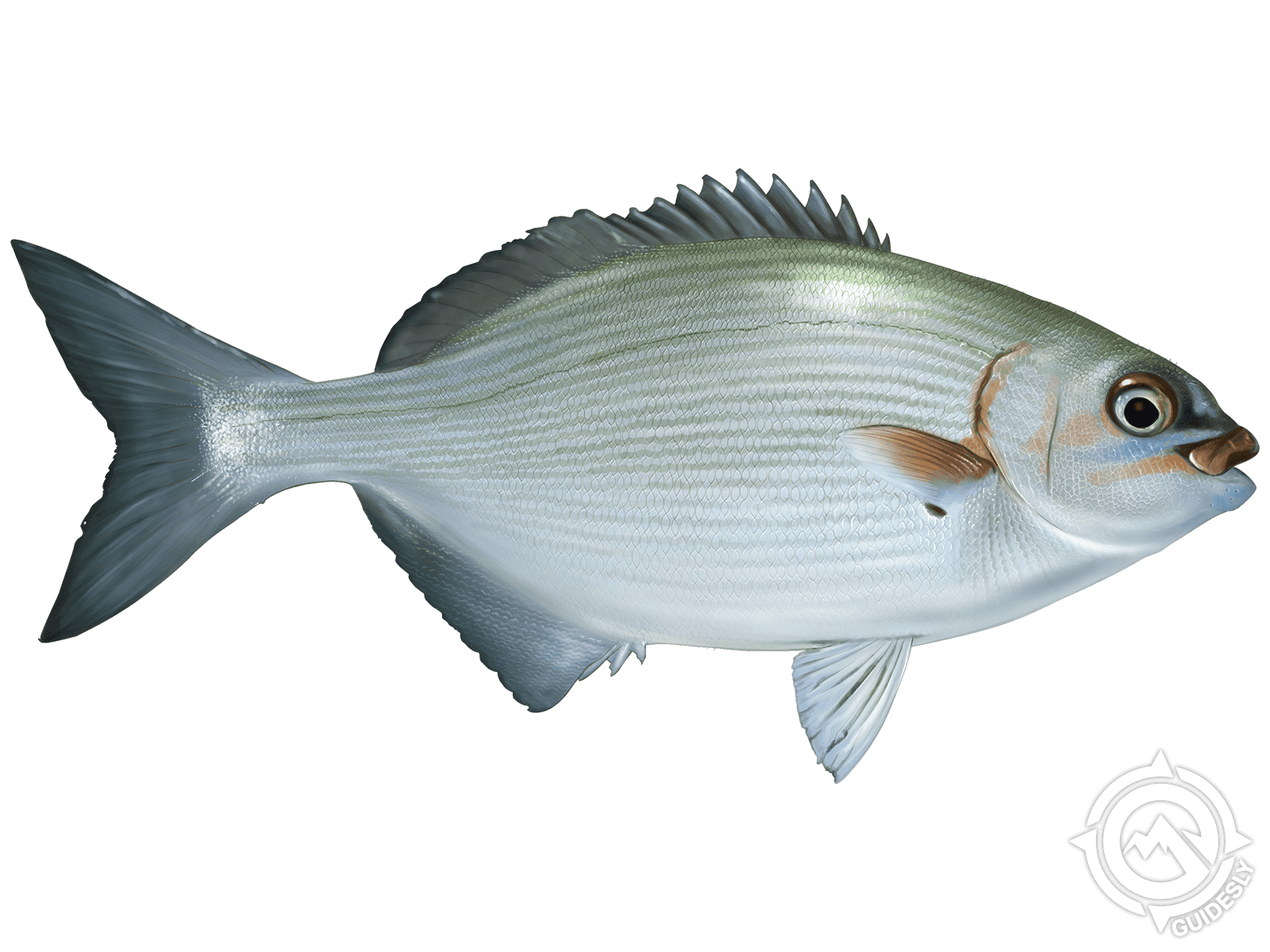
Bermuda Sea Chub (Kyphosus sectatrix) Fish Description
The Bermuda Sea Chub is characterized by having an elliptical-shaped compressed body with steel or blue-grey coloring, striped with pale yellow or gold. Its fins have a duskier coloring, and sometimes it may have white spots. It has a short head and a small mouth.
In outline, it appears to be more round than it really is. Its body is covered with ctenoid scales apart from its snout. In appearance, it looks quite similar to the Yellow Chub, though the latter is a more rare species. To distinguish them from each other, their rays would have to be counted.
Size & Diet
The average size of the Bermuda Sea Chub can range from 12-24 inches, though it can grow up to 30 inches. The biggest on record of the Bermuda Sea Chub weighs 13 pounds, though typically it weighs at 2 pounds. The Bermuda Sea Chub is known to steal bait with its small mouth. Otherwise, this omnivore feeds on algae, snails, small crabs, and mollusks.
Interesting Facts about Bermuda Sea Chub
- The Bermuda Sea Chub has a number of nicknames, including the Beaked Chub, Grey Drummer, Black Snapper, Brim, and Rudder Fish.
- The Bermuda Sea Chub is considered a bony fish.
- The Bermuda Sea Chub is also reported to consume the feces and vomit of Spinner dolphins. It is known to follow ships and feed on the trash from those ships as well.
- Most anglers do not like to catch Bermuda Sea Chub as they are known to excrete feces the moment you catch them on the boat.
- The Bermuda Sea Chub is not the most sought-after fish for eating. That’s because of the smell of its innards and its greenish-gray flesh. However, once cleaned properly and cooked well, it is reported to taste mild, with a smooth and tender texture.
Fishing Technique: How to Catch Bermuda Sea Chub
The Bermuda Sea Chub is not a very popular game fish among anglers. However, if you’re targeting this fish, you can do so by drift fishing. You can use any 15-25 conventional rod with a light spinner, a small hook, and a tiny piece of squid.
To attract a group of this fish, you can drop down a chum bag filled with cut bull minnows. Once you’ve hooked one, you should be able to catch it with a net. Cover yourself or at least your feet if you don’t want feces to land all over you as soon as you get this fish onboard, as it will definitely release poop.
If you are not planning to practice catch and release on this species, you should definitely clean it properly and consume it as soon as you capture it, as its flesh is known to spoil fast.
Habitat and Distribution
The Bermuda Sea Chub is a schooling fish and is most often found congregating with its own and other similar species in clear waters around reefs, harbors, and small ships. It inhabits shallower waters and swims over seagrass beds, sandy or rocky bottoms, and coral reefs. Juvenile chubs are found to settle around floating Sargassum seaweeds.
This fish species occurs globally in the warmer regions of the world’s oceans. It is found both in the eastern and western parts of the Atlantic Ocean, particularly St Helena and Ascension Island, the Azores, and the Canary Islands. Sightings are also reported around Portugal and the waters of the Mediterranean, Bermuda, in the Sargasso Sea, in the Gulf of Mexico and the Caribbean Sea.
In other parts of the globe it can also be found in the waters of southern Japan, Coral Sea, northern New Zealand, eastern Australian coast from Heron Island, Queensland to New South Wales. Populations have also been spotted from Polynesia all the way to Revillagigedo Islands.







