Greenland Shark
Species Details
Somniosus Microcephalus
Somniosidae
Squaliformes
Offshore, Deepwater, Continental Shelves, Continental Slopes
880 - 2200 lbs.
96" - 168"
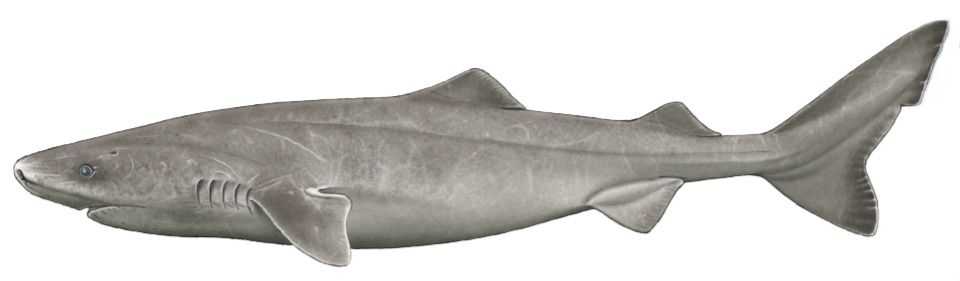
Greenland Shark (Somniosus microcephalus) Description
The Greenland Shark is a large saltwater fish that is considered both a delicacy and a game fish. It has pointy teeth and its lower jaw has square-like teeth. It has an asymmetrical tail and its eyes are small. Their color ranges from brown, black to dark gray and their skin looks like rocks beaten down by the weather, much like that of whales. The Greenland shark is a sleeper shark, these are sharks that are docile and slow-moving. One of its closest relatives is the Bramble Shark.
Size and Diet of the Greendland Shark
The Greenland sharks are known to be scavengers. They eat anything from fish, squid, whales, and even dead mammals such as polar bears or moose. The Greenland shark is one of the biggest fish in the world. It can be as big as 23 feet long and weigh a whopping 2260 lbs. On average, they’re 8 feet long and weigh 1500 lbs.
Interesting Facts About the Greenland Shark
- The Greenland Shark is considered to be the most toxic shark in the world because of its high content of urea.
- Despite being toxic, the Greenland shark’s meat is an exotic food delicacy for Nordic countries. They would cure the shark to remove the urea content by buying it in the ground or hanging it up in racks. It takes 6 months to finish the curing the process, once the meat has a redder-brown color
- 400 years ago, Icelanders were catching Greenland sharks for their oil liver but they didn’t want to waste the meat. At some point, they’ve discovered the curing process and started harvesting for its flesh; cutting the shark can provide 30 to 40 pieces of fillet.
- The taste of the Greenland shark is said to be one of the worst in the culinary world; it may taste like bacon but the after taste reeks of ammonia.
- The Greenland shark is one of the oldest living vertebrates. Their maturity age is estimated to be a slow 120 plus years and the oldest living sharks are said to be 400 plus years old. Scientists believe they grow 1 cm a year.
How to Fish a Greenland Shark
The Greenland sharks may seem docile, but they can show sudden bursts of strength and speed which may catch anglers off guard. They’ll be surprised how thrilling this underrated game fish can be, they might battle this fish out for hours if they catch one, so don’t let the name sleeper shark fool you. So be patient with the fish. To catch the Greenland shark, first, be prepared for the freezing waters. Most of them thrive in the northern parts of the oceans, so make sure you have clothes that can handle the cold. Remember to allocate enough lines that reach 1500 feet deep or longer, then wait for a bite. Once it takes your presentation, reel in with big chunks and stops to take a breather. it will be a gradual process but continue to do this until you get the fish. Once you raise the fish around 300 feet, usually they get tired and easier to pull, this will also be a good time for you to rest.
Here are the recommended gear by anglers for the Greenland shark. Get a rod that can handle a gigantic fish like this, so use 6 to 8 feet trolling rod with a strong braided line of 20-30 lbs attached to a reel with 2200 yards of line to reach the deep waters. For the hooks, use the large and sturdy 12/0 to 16/0 circle hooks.
Being scavengers, you can actually use any carcass but the usually recommended fish baits are pieces of dead salmon, herring, and squid.
Habitat and Distribution of the Greenland Shark
The Greenland shark thrives in the northern Arctic and Atlantic region. In the U.S., their range is from the offshore waters of Maine to North Carolina. They dwell in the deeper part of the oceans, with depth ranges from near-surface to 3900 feet. During winter, Greenland sharks are found nearer the surface and in summer, they can be found in deeper ranges of 600 to 1800 feet. They prefer the cold temperatures between 34°F to 68° F. It is thought that the Greenland sharks are found in every deep part of the oceans of the world, but this needs further proof. Fishing spots for the Greenland shark are continental shelves and slopes, especially in their southern range.







