Deep-Sea Sole
Species Details
Embassichthys Bathybius
Pleuronectidae
Pleuronectiformes
Offshore, Deepwater
6 - 9 lbs.
12" - 19"
Deep-Sea Sole (Embassichthys bathybius) Description
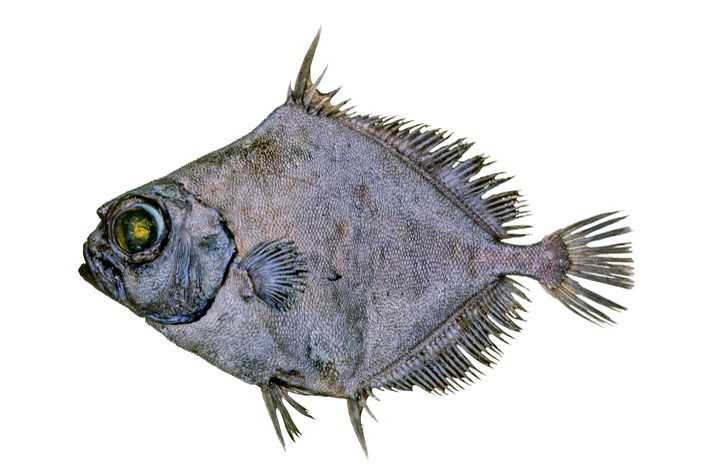
The Deep-Sea Sole is a right-eyed flounder. The eyed side of its body is a marbled brown with darker edges. It is splotched with light blue spots all over, along with the dark brown fins that are also spotted with light blue. Its belly side is dusky brown. Its relatively bright coloring distinguishes it from other right-eyed flounders such as those in the Microstomus species like the Dover Sole.
The head of the Deep-Sea Sole is small, its mouth small, and its eyes big. Its teeth are well-developed on both sides of its jaws, 16 on its eyed side, 21 on its blind side. This makes it quite similar to fish in the Glyptocephalus.
Size & Diet
Most Deep-Sea Sole found to measure 14-20 inches in length and 3 pounds in weight, but this species can grow up to 26 inches in length and 9 pounds in weight. The Deep-Sea Sole typically feeds on amphipods, young bivalves and decapods, copepods marine worms, mollusks, crabs, young herring, shrimps, and polychaete palps.
Interesting Facts about Deep-Sea Sole
- The Deep-Sea Sole is called Shimofurigarei in Japanese and Platija de profundidad in Spanish.
- The Deep-Sea Sole is a prey for the Sablefish.
- The Deep-Sea Sole is classified as a bathydemersal fish species. This means that the Deep-Sea Sole lives and feeds underwater below 650 feet.
- The Deep-Sea Sole was first recorded in 1981 by academics Kunio Amaoka, Kazuo Sakamoto, Koji Abe from Hokkaido, Japan.
- The Deep-Sea Sole belongs to the Pleuronectidae family, like the C-O Sole and the Arrow-Tooth Flounder. Like the others in its species, it spawns with the female laying eggs in mid-water. Once the larvae develop, they sink to the bottom of the oceans.
Fishing Technique: How to Catch Deep-Sea Sole
The Deep-Sea Sole is most frequently caught in July. Though not a lot of information is found on this bathydemersal fish, anglers can fish for them with techniques used for other flatfish. Experienced anglers prefer to fish for flatfish at night when the flatfish are feeding. The key is to target them where a group of them is gathered to feed, and then lure them with light.
In Japan, right-eyed flounders are typically targeted during winter, as fish caught during the cold season tastes best. The recommended gear for flounder fishing in winter is a reel with an adjustable drag and a flexible rod, with a supple 3-meter fishing pole so that the angler can immediately feel the movement when a flatfish comes around. Anglers usually hook with two hooks that are 5 inches apart on the leader. Bait the hook with something live because flatfish are attracted to movement. Drop your line to the bottom, with the bait suspended to the bottom and wait for the flounder to bite. This will take quite a while, so wait for up to 40 seconds for the fish to finish with the bait before setting the hook.
Habitat and Distribution
The Deep-Sea Sole is bathydemersal. It is reported to live on muddy bottoms where it can disappear with its coloring in depths from 135 and 5,900 feet, though many of its population is found deeper at 1,600 to 3,120 feet.
This flatfish is quite rare and is native to the waters of the northern Pacific, ranging from Japan at Cape Erimo, Hokkaido to the Gulf of Alaska and down the Pacific coasts of Canada and the USA, distributed off the coast of southern California to southeastern Alaska and the Bering Sea, particularly the Alaska Peninsula coasts and the western Bering Sea. It has also been found as far south as Mexico.







