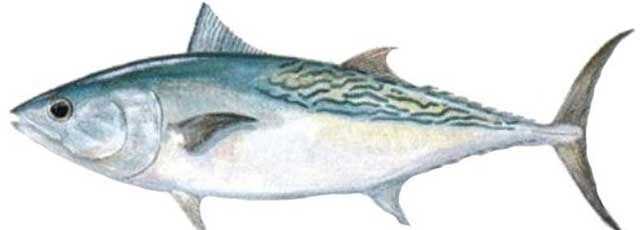
Frigate Tuna
Species Details
Auxis Thazard
Scombridae
Perciformes
Offshore, Warm Water
2 - 4 lbs.
8" - 19"
Frigate Tuna (Auxis thazard) Fish Description
The frigate tuna or frigate mackerel has a strong and elongated body and a single line of tiny pointed teeth. Its dorsal fins have a well-defined gap in between them. Its second dorsal fin is tiny and has a row of even tinier finlets, eight in total. Its anal fin is also characteristically small, and its pectoral fins quite short.
Its coloring on the back is a deep metallic blue-black, and it fades to a kind of purple approaching the head. It is hard to distinguish it from another species in its genus, the bullet tuna or bullet mackerel. One quick way to distinguish them is to look at the height of the corselets of the two under their second dorsal fins. The ones on the frigate tuna are so much shorter compared to the bullet tuna, only one to five scales, compared to the bullet tuna’s height of ten or more scales.
Size and Diet
The frigate tuna measures around 12 inches on average and weighs 2 pounds. But it can reach a length of 22 inches and weight of 10 pounds. This fish species is reported to live up to 5 years.
The frigate tuna, considered omnivores, normally consumes smaller fish, planktonic crustaceans, squids, and stomatopod larvae. It is also reported to feed on the young of its own species.
Interesting Facts About the Frigate Tuna
- The frigate tuna is considered commercially significant in many parts of the world. Its flesh, however, is known to quickly deteriorate and is characterized by its dark color and oiliness. Commercial fishers primarily use it as bait.
- The frigate tuna is also a food source for other fish species such as swordfish, blue marlins, and sailfish. It is also part of the diet of animals such as seals and sea lions, dolphins, mako sharks, and pelicans.
- The spawning season of this fish species depends on where they’re located as they are widely distributed. For example, in the southern part of the Indian Ocean, they can spawn from August to April, while in the northern parts they can spawn from January to April.
- Mature frigate tuna can occur in eastern Pacific all year round. However, off Costa Rica, mature frigate tuna spawn mostly heavily during December up to April, and in the Japanese waters, their spawning peaks around July.
- The female frigate tuna can produce 200,000 to 1 million eggs, depending on its size, as its size at maturity greatly varies depending on its location.
- The frigate tuna is known to be highly migratory, schooling with other Scombrids along the coastal and oceanic waters.
Fishing Technique: How to Catch Frigate Tuna
The frigate tuna, like other tuna and mackerel fish species, feed when the currents of the ocean are warm, so that’s when it’s great to target them when fishing.
The frigate tuna is known to be quite aerodynamic, so anglers will benefit from using a high speed reel like the Shimano Saragosa, Stella or Daiwa Saltiga, or Penn Slammer 3 when fishing for this species. Anglers should consider using a 3000 or 3500 threadline reel for the frigate tuna. The key to catching this fish species is to retrieve it as fast as possible. However, varying your action such as employing sudden stop might also attract the fish that you're targeting as it fools the fish you're targeting.
More experienced anglers can also consider big baitcasters, as they guarantee casting accuracy and distance. They are a little hard to master, so beginners might want to steer clear of them.
As for the lure, a white metal lure attracts the frigate tuna the best. Chrome works well, too, but this fish species seem to be partial to the white color, especially during low light situations.
A school of this fish species, along with other Scombrids, can typically be found in the shallower areas of oceanic waters. Oftentimes, seeing schools of scombrids is an excellent way of finding an even bigger game fish.
Habitat and Distribution
The frigate tuna is known to be a cosmopolitan fish species. It exists worldwide in coastal and oceanic waters. Its eggs and larvae are pelagic, but its adults are epipelagic, neritic, and oceanic, preferring to stay in shallow coastal waters and water columns.
This fish species can be found in tropical and subtropical waters. It is reported to rarely occur in the Atlantic Ocean. The subspecies that resides in the eastern part of the Pacific Ocean are now distinguished from the frigate tuna with the scientific name, Auxis brachydorax.







